HIV/AIDS Awareness in the PH Drops
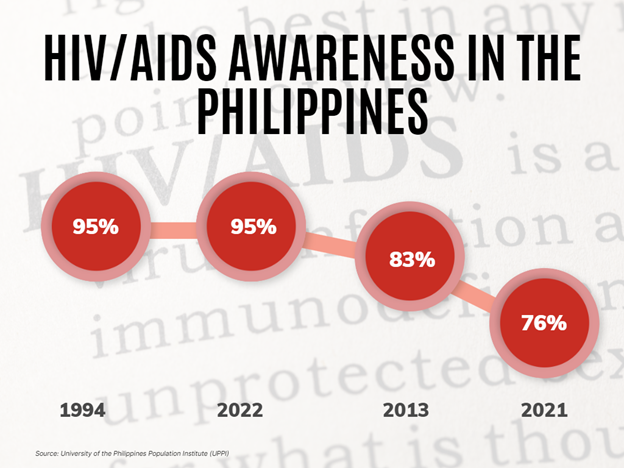
While the HIV and AIDS cases in the Philippines is rising, the percentage of young Filipinos who are aware of the disease is dropping. According to the Young Adult Fertility and Sexuality Study (YAFS5) conducted in 2021 by the University of the Philippines Population Institute (UPPI), only 76% of 15 to 24 year-olds had heard of HIV and AIDS, a 19% drop from 95% in 1994.
The disease awareness was still at 95% in 2002, and started to decrease to 83% in 2013, the study said. This finding, according to UPPI, is alarming because the lack of understanding and awareness of HIV and AIDS greatly affects the efforts to stop the rising infection rate in the country. Given the country’s 237% increase in annual new infections between 2010 and 2020, the Philippines has the fastest increasing HIV epidemic in Asia and the Pacific and is one of eight nations responsible for more than 85% of new HIV infections in the region, according to the Department of Health (DOH).
What is HIV/AIDS?
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US CDC), is a virus that targets the body’s immune system and, if left untreated, can result in AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
How is HIV Spread?
HIV transmission is the spread of HIV from one person to another. Only specific bodily secretions from an HIV-positive person can transmit the virus. These are:
- Blood
- Semen
- Pre-seminal fluid
- Vaginal fluids
- Rectal fluids
- Breast milk
The only way to contract HIV is by coming into touch with bodily fluids that are HIV-positive. HIV is mostly spread by:
- Having sex without using a condom with someone who has HIV
- Sharing needles or syringes with an HIV-positive person who is using injectable drug equipment
Perinatal transmission of HIV is the term used to describe the spread of HIV from an HIV-positive woman to her unborn child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
Important Note
You cannot contract HIV via shaking hands or embracing an HIV-positive individual. Additionally, youcannot contract HIV through coming into contact with anything used by an HIV-positive person, such as dishes, toilet seats, or doorknobs. HIV cannot be carried by mosquitoes, ticks, or other blood-sucking insects, nor is it spread by the water or the air.
What are the Stages of HIV?
Stage 1: Acute HIV Infection
- Appears 2-4 weeks after HIV infection
- Patient experience flu-like symptoms (fever, headache, rash)
- The risk of HIV transmission at this stage significantly rises due to extremely high levels of HIV in the blood
- Starting antiretroviral therapy of ART at this point may have a huge positive impact on the patient’s health
Stage 2: Chronic HIV Infection
- Also called asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency
- HIV continues to replicate in the body but at low levels
- Without ART at this stage, the infection typically progresses to AIDS in 10 years or more, or sooner in some patients
- Patients taking ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have minimal chance of passing the virus through sex
Stage 3: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
- Last and most severe stage of HIV infection
- Immune system is already damaged, and the patient cannot anymore fight serious infections
- Patient has a high viral load and can infect others
- Patient often live for 3 years without treatment
How to Reduce your Risk?
Limiting the number of your sexual partner, correct use of condom when having sex, and not sharing injection equipment to lowers your risk of contracting HIV.
Additionally, you may discuss pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with your doctor. PrEP is a method of HIV prevention for those who do not currently have the virus but who are at high risk of contracting it.
The risk of perinatal HIV transmission is decreased by HIV medications given to HIV-positive women during pregnancy, childbirth, and to their newborns after birth. Breastfeeding must be avoided after delivery since breast milk contains HIV so as not to transmit the virus to the newborn.
HIV Testing
Getting tested is the only way to find out if you have HIV. People who are at higher risk for HIV should typically be tested every year. Men who identify as gay or bisexual and are sexually active may benefit from more frequent testing, such as every three to six months.
Treatment
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the use of HIV medications to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV treatment regimen) every day.
ART is advised for all HIV-positive individuals as it decreases the amount of HIV in the body (called the viral load) by preventing it from replicating. Lower HIV levels in the body safeguards the immune system and prevents the development of AIDS. HIV medications help patients with HIV live a longer, healthier lives, but it cannot totally cure HIV.
The main goal of ART is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means the level of HIV in blood is too low. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have practically no risk of transmitting the virus to their partner.
World AIDS Day 2022: Equalize
Since 1988, World AIDS Day is observed every first of December to spread awareness about the AIDS pandemic and encourage progress in HIV/AIDS prevention, treatment, and care worldwide. This year’s theme, “Equalize” aims to address the inequalities that hinder the progress in ending AIDS. World leaders are urged to acknowledge and act on these inequalities, equalize access to vital HIV services, especially for children and key populations and their partners, including men who have sex with men, transgender people, drug users, sex workers, and those who are incarcerated.
References:
Peña, K. D. (2022, October 19). As AIDS, HIV awareness among PH youth declines, cases, deaths rise. INQUIRER.net. https://newsinfo.inquirer.net/1681539/as-aids-hiv-awareness-among-ph-youth-declines-cases-deaths-rise
EQUALIZE – WORLD AIDS DAY 2022. (n.d.). UNAIDS. Retrieved November 25, 2022, from https://www.unaids.org/en/2022-world-aids-day
HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC. (n.d.). https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/index.html
Understanding HIV | HIVinfo. (n.d.). https://hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv
